Tired of slow charging and carrying a tangled mess of different adapters? This daily wait and clutter is frustrating. USB Power Delivery (PD) offers a universal, high-speed solution for many devices.
USB Power Delivery (PD) is a fast charging standard using the USB-C port. It supports up to 240W, dynamically adjusting voltage and current. This means faster, more efficient charging for phones, laptops, and more, simplifying your tech life and reducing e-waste.
This standard isn’t just about speed; it’s about smart, versatile power delivery. As someone working in power adapter design at Quankang Technology for years, I’ve seen its impact grow. It’s truly exciting to see how it’s reshaping our approach to power. Let’s look closer at how USB PD works and why it’s becoming so important for everyone, from product designers like me to everyday users.
What Exactly is the USB PD Protocol and Why Does It Matter So Much?
Feeling overwhelmed by the different chargers needed for every gadget? It’s annoying and frankly, quite wasteful. The USB PD protocol, developed by the USB Implementers Forum (USB-IF), aims to simplify all this with one powerful, widely accepted standard.
The USB Power Delivery (PD) protocol is a universal fast charging standard. It uses the versatile USB-C interface for high-power charging, now supporting up to 240W. It smartly adjusts power delivery based on what each specific device needs, a big step up from older USB protocols.
The USB PD protocol is a big deal because it brings order to the chaos of charging. Before PD, we had so many different charging standards, often proprietary. This meant users needed a drawer full of chargers. I remember when we first started discussing PD at Quankang; the potential for a unified standard was a frequent topic. The latest version, PD 3.1, is particularly impressive. It can provide higher voltage levels, going up to 48V. This expansion means it can now comfortably power a much wider range of devices. We’re not just talking about smartphones anymore. Laptops, tablets, gaming consoles, and even some small home appliances can benefit.
Key Features of USB PD
As designers and manufacturers of power adapters, we pay close attention to these specifications:
- High Power Capability: From a few watts for small gadgets to 240W for power-hungry devices.
- Voltage Negotiation: Devices and chargers "talk" to each other to determine the optimal power level.
- Single Cable Simplicity: USB-C is reversible and versatile, handling both data and power.
I recall working with a client who was developing a new portable workstation. They needed serious power, but also a sleek design. Traditional power bricks were too bulky. USB PD 3.1 was the perfect solution. We helped them design a compact yet powerful PD adapter that met their needs. This shift towards a universal standard makes life easier for consumers and pushes companies like ours at Quankang to create more efficient and innovative power solutions. It allows us to focus on quality and performance, knowing the underlying standard is robust and widely adopted. We see this as a positive change for the entire electronics industry.
How Do USB PD’s Technical Features Give It a Real Edge in Charging?
Are you curious about what makes USB PD technically superior to older charging methods? It’s not just about more power; it’s about smarter power. The way it communicates and adapts is key.
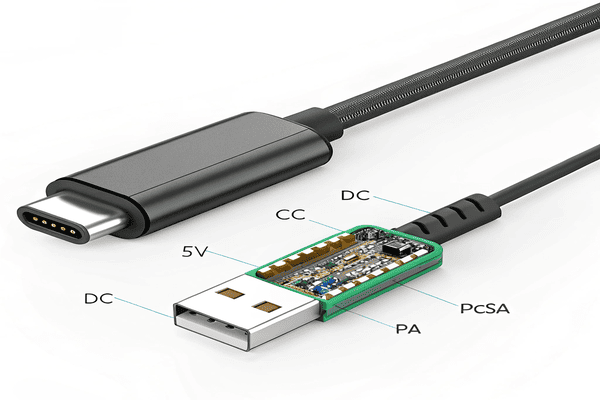
USB PD uses the Configuration Channel (CC) pins in the USB-C connector for communication. This is different from older protocols like QC that used D+/D- pins. This allows for flexible, dynamic voltage adjustments from 5V up to 20V, or even higher with newer specs like 28V, 36V, or 48V.
The use of CC pins for power negotiation is a core strength of USB PD. This dedicated communication channel allows the charger and the device to have a sophisticated dialogue. They can agree on the best voltage and current for efficient and safe charging. For us at Quankang, designing adapters that correctly implement this communication is crucial. It requires precision in our circuitry and firmware. I remember when we were first R&D-ing PD adapters, ensuring this handshake worked flawlessly across a wide range of devices was a top priority. It’s more complex than just supplying a fixed voltage.
Dynamic Power Adjustment in Action
This flexibility means devices get exactly the power they need.
- Low Power Devices: A smartphone might request 9V.
- High Power Devices: A laptop could ask for 20V, or with PD 3.1 Extended Power Range (EPR), even up to 48V for more demanding applications.
This intelligent power distribution prevents overcharging and can improve the lifespan of batteries. For example, a device can request a lower voltage when its battery is nearly full to reduce stress. This is a significant advantage over simpler charging protocols that might just push a constant high current. Our team often discusses how these features translate into better user experiences, and we design our adapters to fully support these nuanced power conversations. We want the end-user to just plug it in and know their device is charging optimally and safely. That’s the goal we strive for with every PD adapter we manufacture.
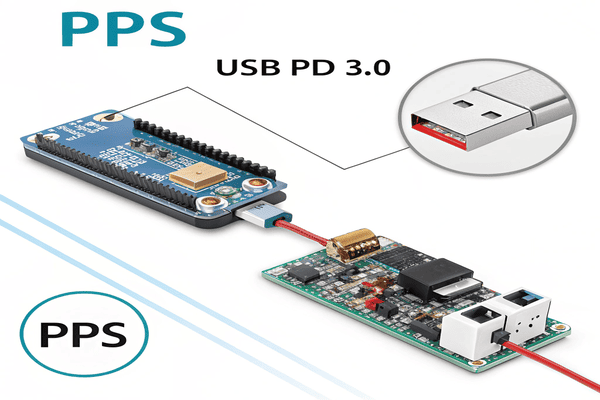
What Makes Programmable Power Supply (PPS) Fast Charging So Smart and Efficient?
Ever notice your phone getting warm during fast charging? Sometimes, rapid charging can generate excess heat. Programmable Power Supply (PPS), a feature in USB PD, directly addresses this issue, making charging smarter.
PPS is a feature introduced in USB PD 3.0 and newer versions. It allows for very fine, step-by-step adjustments in voltage and current during charging. For example, it can adjust voltage in tiny 20mV steps, helping to reduce battery heat and energy loss, thereby boosting charging efficiency.
The introduction of PPS was a significant step forward for fast charging. Before PPS, USB PD already offered different fixed voltage levels. But PPS allows for a much more granular, almost continuous, adjustment of voltage, typically from 3.3V up to 21V, in small increments. This means the charger can supply a voltage that very closely matches what the battery needs at any given moment. Why is this important? When a charger supplies a voltage that’s much higher than what the battery can efficiently accept, the excess energy is often converted into heat within the device. This isn’t just inefficient; it can also degrade the battery over time.
Benefits of PPS
Here’s how PPS helps:
| Feature | Benefit | Impact on Device |
|---|---|---|
| Fine Voltage Steps | Reduces energy conversion loss in the device | Less heat generation |
| Dynamic Current | Adapts to battery’s state of charge | Improved charging speed |
| Battery Health | Minimizes stress on the battery cells | Potentially longer life |
At Quankang, when we design PD chargers with PPS support, we focus on the precision of the output. It’s a more complex design than a standard fixed-voltage charger. I recall a specific project where a client, a smartphone manufacturer, wanted to highlight "cool charging" as a key feature. PPS was essential for this. By implementing PPS correctly in our adapters, their phones could charge quickly without becoming uncomfortably warm. This feature is particularly common and beneficial for smartphones, where battery health and user comfort are paramount.
It’s a great example of how USB PD continues to evolve for better performance and safety.
What Do We Need to Know About Adapters and Cables for USB PD?
So, you’ve got a device that supports USB PD fast charging. That’s great! But to actually use it, you also need the right adapter and cable. Not all USB-C accessories are created equal.
Devices and chargers supporting USB PD are now widespread. Chargers typically use USB-C ports for compatibility. Importantly, USB-C to USB-C or USB-C to Lightning cables often have an embedded E-Marker chip. This chip communicates the cable’s maximum current capacity (e.g., up to 5A) to the charger and device.
The role of the E-Marker (Electronically Marked Cable) chip is critical for safe and efficient high-power charging. For currents up to 3A, a standard USB-C cable might suffice. But when you go above 3A, up to 5A (which means up to 100W at 20V), an E-Marker chip is mandatory according to USB PD specifications. This chip essentially tells the charger, "I’m a cable capable of handling 5A safely." Without this information, a PD charger will typically limit the current to 3A to prevent potential damage to a lower-spec cable.
For power levels above 100W, especially with the new PD 3.1 standard enabling up to 240W (48V at 5A), the cable requirements become even more stringent. While 5A is the current E-Marker standard maximum, reaching the full 240W (EPR – Extended Power Range) means both the charger and the device must support these higher voltages, and the cable must be rated for 5A and be EPR-compliant. Some manufacturers might use proprietary protocols for current beyond 5A in very specific controlled ecosystems, but for general USB PD compliance, 5A is the typical E-Marker declared maximum.
As a power adapter manufacturer, we at Quankang always advise our clients on the importance of pairing our PD adapters with good quality, certified cables. A poorly made cable can not only slow down charging but can also be a safety hazard. I’ve seen cases where using a cheap, non-compliant cable with a powerful PD charger led to poor performance or even cable failure. We often test our adapters with a variety of cables to ensure compatibility and safety. It’s an ecosystem where every component – the device, the charger, and the cable – needs to work together correctly.
How Far Can USB PD 3.1 Really Push Charging Power and Applications?
We’ve seen USB PD grow from a convenient charging standard to a real powerhouse. But how much further can it go? The latest USB PD 3.1 revision gives us a clear answer: much further!
The introduction of the USB PD 3.1 protocol significantly increases the maximum power capability to 240W. This major boost expands its application areas well beyond common mobile phones and tablets. It can now effectively power gaming devices, high-performance laptops, and even some small home appliances.
This jump to 240W is a game-changer. Previously, the 100W limit of USB PD 3.0 was sufficient for most ultrabooks and many standard laptops, but power-hungry machines like mobile workstations, gaming laptops, or large displays often needed their own bulky, proprietary power bricks. PD 3.1, with its Extended Power Range (EPR) feature, introduces new fixed voltage levels of 28V, 36V, and 48V, allowing for this higher power delivery while still typically using a 5A current.
At Quankang, the development of PD 3.1 solutions has been an exciting challenge. Designing a compact adapter that can safely and efficiently deliver 240W requires careful thermal management, advanced component selection (like GaN technology), and robust safety features. I remember our engineering team spending weeks optimizing a 240W reference design. The goal was not just to deliver power, but to do it in a form factor that’s still convenient for users.
Emerging Applications for USB PD 3.1:
- Gaming Laptops: Many models require well over 100W.
- Mobile Workstations: For professionals needing portable power.
- Large 4K/8K Monitors: Some can be powered directly via USB-C.
- Docking Stations: Single-cable solutions for power, data, and display.
- Small Appliances: Potentially e-bikes, power tools, or portable kitchen gadgets.
Many leading electronics manufacturers, including well-known brands for laptops like Huawei, Lenovo, and Samsung, are already adopting or exploring PD 3.1 for their high-power devices. This ensures fast charging while maintaining strict safety standards. For us, it means being ready to supply adapters that meet these new demands, helping our clients bring innovative products to market faster. It’s a continuous evolution, and we’re committed to staying at the forefront of power delivery technology.
What’s Next for USB PD as It Becomes the Global Charging Standard?
USB PD has made incredible progress in becoming a truly universal charging solution. But what does the future hold? Is it set to completely take over, and what challenges or developments can we expect?
As the USB PD protocol solidifies its position as the global fast charging standard, its application scope continues to broaden. Many electronics manufacturers are accelerating the launch of devices supporting PD 3.1, covering smartphones, laptops, smart home devices, and more. The trend is clear: wider adoption and more power.
The journey of USB PD towards becoming a de facto global standard is well underway. Regulatory bodies in some regions are even mandating USB-C as a common charging port, which naturally promotes PD adoption. At Quankang, we see this as a very positive development. It simplifies things for consumers, reduces electronic waste from redundant chargers, and allows us manufacturers to focus on innovation within a common framework. We’ve seen a surge in inquiries from companies looking to integrate PD into a wider array of products, beyond the usual consumer electronics.
Looking ahead, I believe we’ll see several key trends:
- Increased Power Density: Expect even smaller and more efficient PD chargers, likely driven by further advancements in semiconductor technology like GaN (Gallium Nitride) and SiC (Silicon Carbide). Our R&D team is constantly exploring these materials.
- Smarter Power Management: Beyond PPS, we might see more sophisticated algorithms for optimizing charging based on usage patterns, battery health, and even ambient temperature.
- Wider Integration: PD could become standard in more diverse areas, like automotive (charging passenger devices), medical equipment, and industrial tools. I once worked with a company developing specialized field equipment; reliable PD charging was a key requirement for them.
- Focus on Sustainability: With a universal standard, there’s a greater push for durable, repairable, and recyclable chargers and cables.
As technology develops, the USB PD protocol is expected to become the mainstream solution for an even greater number of high-power application scenarios. It’s not just about charging anymore; it’s about intelligent power delivery. For us at Quankang, our commitment is to continue sharing our expertise and experience. We aim to provide robust support and assistance to other companies in the industry, helping them navigate the complexities of PD implementation and contribute to the success and growth of the entire ecosystem. The future of charging is looking very USB PD-centric, and that’s exciting for all of us.
Conclusion
USB PD, especially with PD 3.1, offers powerful, flexible, and increasingly universal charging. It’s simplifying how we power devices, from phones to high-performance laptops, becoming a core industry standard.