Power is everywhere in our lives. From smartphones to industrial machines, different devices need different power sources. But do you know all the types available? Let’s explore the standard power supply options you’ll encounter.
Power supplies convert electrical energy to usable forms for devices. The main types include AC adapters, DC power supplies, uninterruptible power supplies (UPS), linear supplies, and switched-mode power supplies (SMPS). Each serves a specific purpose based on voltage, current, and application needs.
Understanding these categories helps whether you’re designing electronics or just curious about power sources. The right choice ensures device safety, efficiency, and performance. Let’s examine each type in detail.
What are AC power adapters, and where are they used?
You’ve used AC adapters daily without realizing it. That small box between your laptop plug and the outlet? Exactly what we mean.
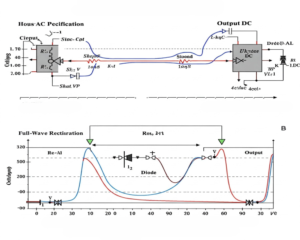
AC adapters (alternating current adapters) convert wall outlet AC power (100-240V) to lower DC voltages (5-48V) for electronics. Common in laptops, routers, and small appliances, they provide safe, regulated power through compact external units.
AC adapters dominate consumer electronics for good reasons:
Key features:
- Input: 100-240V AC (works worldwide)
- Output: 3-48V DC (device specific)
- Power ratings: 5W-300W typically
Advantages: - Safe low-voltage output
- Compact and portable
- Cost-effective solution
Common applications:
| Device Type | Typical Voltage | Example Products |
|---|---|---|
| Mobile devices | 5V | Phones, tablets |
| Home electronics | 9-12V | Routers, printers |
| Laptops | 15-20V | Business/consumer notebooks |
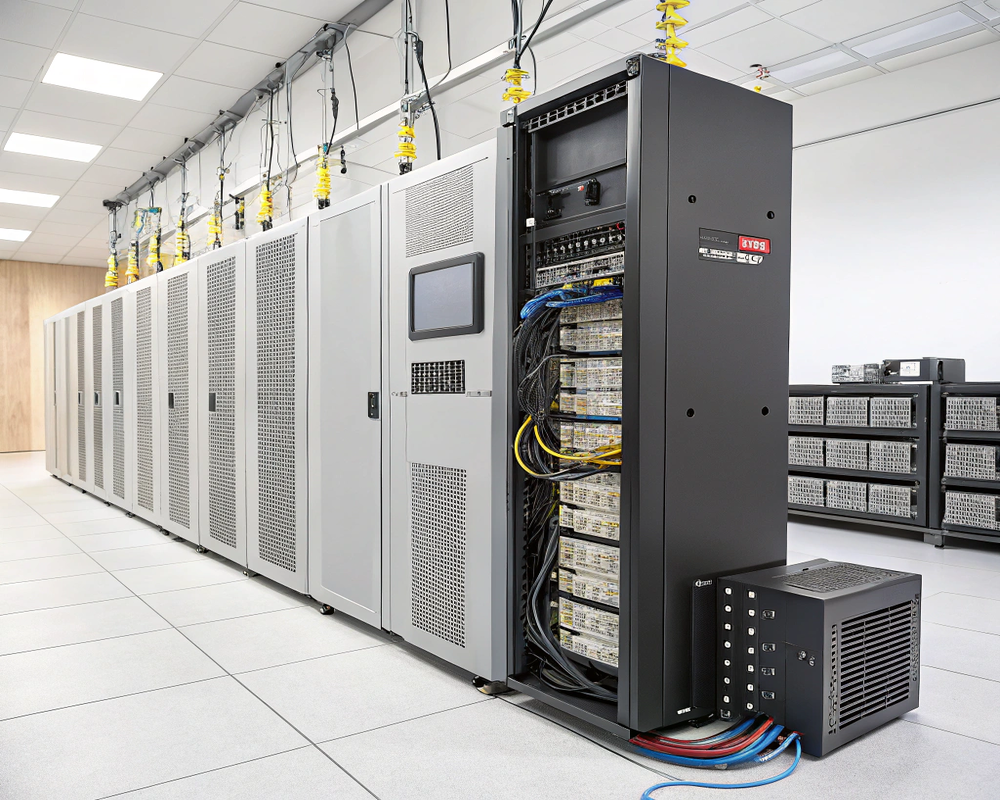
The wall-wart design saves space in devices while meeting international safety standards. At our factory, we test each unit for 100% load capacity and efficiency before shipping.
How do DC power supplies differ from AC adapters?
Factory floors and labs buzz with DC power equipment. Unlike household adapters, these handle tougher jobs.
DC power supplies convert AC to stable direct current with precise voltage/current control. Used in industrial automation, testing, and telecom systems, they offer adjustable outputs (0-60V commonly) with higher power capacity (up to 3000W).

Industrial DC solutions focus on reliability and precision:
Technical breakdown:
- Regulation: <1% voltage fluctuation
- Interfaces: Digital controls, remote monitoring
- Protection: Over-current/voltage safety cutoffs
Comparison with AC adapters:
| Feature | AC Adapters | DC Power Supplies |
|---|---|---|
| Output type | Fixed DC | Adjustable DC |
| Power range | 5-300W | 50-3000W+ |
| Cooling | Passive | Active fans |
We recently designed a 2000W modular DC system for 5G base stations. The water-cooled units maintain 95% efficiency even at full load—critical for continuous operation.
Why choose UPS systems for critical equipment?
Hospitals and data centers can’t afford blackouts. That’s where uninterruptible power supplies become lifesavers.
UPS systems provide emergency power during outages using batteries. They protect sensitive equipment from power interruptions (offline UPS) or fluctuations (online UPS). Typical backup lasts 5-30 minutes—enough for safe shutdowns or generator start-up.
UPS selection depends on protection needs:
Types comparison:
| Type | Response Time | Power Conditioning | Best For |
|---|---|---|---|
| Offline | 2-10ms | Basic | Home PCs |
| Line-interactive | <4ms | Voltage regulation | Small offices |
| Online | 0ms | Full isolation | Medical equipment |
Key specifications:
- Runtime vs load percentage (non-linear relationship)
- Battery type: Lead-acid vs lithium-ion
- Transfer switches: Automatic vs manual
Our hospital’s UPS project in Malaysia uses modular lithium batteries. The system scales easily while maintaining 99.999% uptime, proving that cost isn’t everything when lives depend on power.
Conclusion
From tiny AC adapters to industrial UPS systems, power supplies keep our world running. Understanding these options helps choose the right solution for any electrical need.